Spirometry (PFT)
Spirometry (PFT)
The tests determine how much air your lungs can hold, how quickly you can move air in and out of your lungs.
The tests can diagnose lung diseases, measure the severity of lung problems, and check to see how well treatment for a lung disease is working.
Lung Function Tests Are Done To:
- Determine the cause of breathing problems.
- Diagnose certain lung diseases, such as asthma or chronic obstructive. pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Evaluate a person’s lung function before surgery.
- Check the lung function of a person who is regularly exposed to substances. such as asbestos that can damage the lungs.
- Check the effectiveness of treatment for asthma and other lung diseases.
- The testing may take from 5 to 30 minutes, depending upon how many tests are done.
How The Test Is Performed?
Spirometry measures airflow. By measuring how much air you exhale, and how quickly, spirometry can evaluate a broad range of lung diseases. In a spirometry test, while you are sitting, you breathe into a mouthpiece that is connected to an instrument called a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount and the rate of air that you breathe in and out over a period of time.
How to Prepare for the Test?
- Do not eat a heavy meal before the test
- Do not smoke for 4 – 6 hours before the test
- you need to stop using bronchodilators or inhaler medications
- You may have to breathe in medication before or during the test.
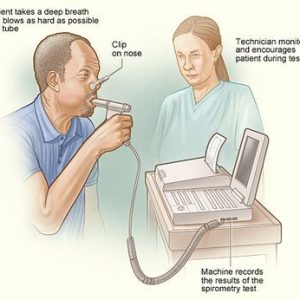
How The Test Will Feel?
Since the test involves some forced breathing and rapid breathing, you may have some temporary shortness of breath or lightheadedness. You breathe through a tight-fitting mouthpiece, and you’ll have nose clips.
Why The Test is Performed?
Pulmonary function tests are done to:
Diagnose certain types of lung disease (such as asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema)
Find the cause of shortness of breath
Measure whether exposure to chemicals at work affects lung function
Check lung function before someone has surgery
It also can be done to:
Assess the effect of medication
Measure progress in disease treatment
Normal Results
Normal values are based upon your age, height, ethnicity, and sex. Normal results are expressed as a percentage. A value is usually considered abnormal if it is less than 80% of your predicted value. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific
Test Results
Different measurements that may be found on your report after spirometry include:
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Forced expiratory volume (FEV)
Forced expiratory flow 25% to 75%
Functional residual capacity (FRC)
Maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV)
Residual volume (RV)
Peak expiratory flow (PEF).
Slow vital capacity (SVC)
Total lung capacity (TLC)
What Abnormal Results Mean?
Abnormal results usually mean that you may have some chest or lung disease. Some lung diseases (such as emphysema, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and infections) can make the lungs contain too much air and take longer to empty. These lung diseases are called obstructive lung disorders.
Other lung diseases make the lungs scarred and smaller so that they contain too little air and are poor at transferring oxygen into the blood. Examples of these types of illnesses include:
Extreme overweight
Fibrosis of the lungs
Lung cancer
Sarcoidosis
Book an Appointment
Need to schedule a visit with one of our specialists? It’s easy! Just click on “Book an Appointment” button below.
Book your appointment online today and get the care you need from our qualified healthcare professionals.
Contact Info
Address
24-A Shah Complex, opposite OPD gate of SMHS Hospital, Karan Nagar, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir 190010
Phone
94190 07775 | 01942504864
lungkashmir@rediffmail.com
allergy.sleepmed@gmail.com
